medial meniscus tear diagnostic test|special tests for meniscus tear : agent There are no risks to your knee from your provider performing a McMurray test. You might feel a little pain or discomfort during the test, but even if your meniscus . See more The PodiaClave+ is specifically designed for the clinic based podiatrists and chiropodists, easy to use, reliable and cost-effective, its’ out-standing performance comes from having more than 30 years of high quality .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Utilizing steam under pressure, this method effectively sterilizes a wide array of medical tools and supplies. This guide provides an in-depth look at steam sterilization, highlighting its principles, processes, and its critical role in .
The McMurray test is a series of movements to check your symptoms and range of motion (how far you can move your knee joint). The test is simple and includes the following steps: 1. You’ll lay on your back. 2. Your provider will bend your knee to 90 degrees perpendicular to the rest of your body (about where it . See more
You don’t need to do anything to prepare for a McMurray test. Just visit your provider as soon as possible if you’ve injured your knee or you notice any new . See more
Try to relax while your provider is moving your leg and knee during a McMurray test. Because the McMurray test is a series of physical motions, make sure . See more
A McMurray test is usually a first step in treating your knee. If your provider feels or hears anything in your knee during a McMurray test, they’ll recommend either . See moreThere are no risks to your knee from your provider performing a McMurray test. You might feel a little pain or discomfort during the test, but even if your meniscus . See moreMcMurray's test is used to determine the presence of a meniscal tear within the knee. Technique. Patient Position: Supine lying with knee completely flexed. Therapist Position: on the side to .The McMurray test is a series of knee and leg movements healthcare providers use to diagnose a torn meniscus. It’s an in-office physical exam, which means your provider can perform it without any special equipment or a separate appointment.
McMurray's test is used to determine the presence of a meniscal tear within the knee. Technique. Patient Position: Supine lying with knee completely flexed. Therapist Position: on the side to be tested. Proximal Hand: holds the knee and palpates . But X-rays can help rule out other problems with the knee that cause similar symptoms. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This uses a strong magnetic field to produce detailed images of both hard and soft tissues within your knee. It's the best imaging study to detect a torn meniscus.
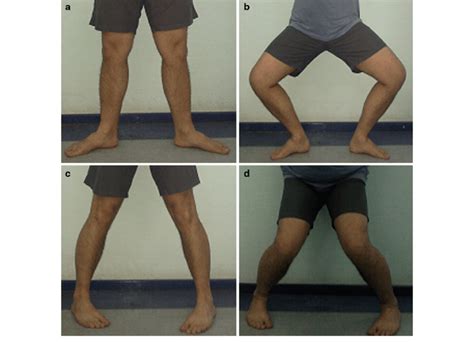
Ege's test helps diagnose a meniscus tear in the knee. It involves putting weight on the knee in a squatting position under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Pain or a clicking noise may indicate a meniscus tear. Introduction. The lateral and medial menisci are crescent-shaped fibrocartilaginous structures that collectively cover approximately 70% of the articular surface of the tibial plateau and primarily function in load transmission and shock absorption through the tibiofemoral joint. Meniscal tears are common sports-related injuries in young athletes and can also present as a degenerative condition in older patients. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with joint line tenderness and a positive McMurray's test, and can be confirmed with MRI studies.
Meniscal injuries can occur in isolation or in association with collateral or cruciate ligament tears. (See "Medial (tibial) collateral ligament injury of the knee" and "Anterior cruciate ligament injury".) The diagnosis and treatment of meniscal injuries will be reviewed here.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. An MRI scan assesses the soft tissues in your knee joint, including the menisci, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. MRI is the preferred method of diagnosing acute meniscus tears (tears that occur due . Meniscus Tear Diagnosis. To diagnose a meniscus tear, your doctor will give you a thorough exam and ask how you got your injury. They'll check your knee to see if there's any tenderness.The medial meniscus sits on the inside of the knee and the lateral meniscus sits on the outside of the knee. Meniscus tears usually take place when an athlete twists or turns their upper leg while their foot is planted and their knee is bent. Occasionally menisci can develop as a block or disk shape, which is called a discoid meniscus.
lab pipettes for sale
The McMurray test is a series of knee and leg movements healthcare providers use to diagnose a torn meniscus. It’s an in-office physical exam, which means your provider can perform it without any special equipment or a separate appointment.McMurray's test is used to determine the presence of a meniscal tear within the knee. Technique. Patient Position: Supine lying with knee completely flexed. Therapist Position: on the side to be tested. Proximal Hand: holds the knee and palpates .
But X-rays can help rule out other problems with the knee that cause similar symptoms. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This uses a strong magnetic field to produce detailed images of both hard and soft tissues within your knee. It's the best imaging study to detect a torn meniscus.
Ege's test helps diagnose a meniscus tear in the knee. It involves putting weight on the knee in a squatting position under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Pain or a clicking noise may indicate a meniscus tear.
lab pipettes hood
Introduction. The lateral and medial menisci are crescent-shaped fibrocartilaginous structures that collectively cover approximately 70% of the articular surface of the tibial plateau and primarily function in load transmission and shock absorption through the tibiofemoral joint. Meniscal tears are common sports-related injuries in young athletes and can also present as a degenerative condition in older patients. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with joint line tenderness and a positive McMurray's test, and can be confirmed with MRI studies. Meniscal injuries can occur in isolation or in association with collateral or cruciate ligament tears. (See "Medial (tibial) collateral ligament injury of the knee" and "Anterior cruciate ligament injury".) The diagnosis and treatment of meniscal injuries will be reviewed here.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. An MRI scan assesses the soft tissues in your knee joint, including the menisci, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. MRI is the preferred method of diagnosing acute meniscus tears (tears that occur due .
Meniscus Tear Diagnosis. To diagnose a meniscus tear, your doctor will give you a thorough exam and ask how you got your injury. They'll check your knee to see if there's any tenderness.
squat test for meniscus tear
special tests for meniscus tear
lab pipettes plastic
Prepreg is best laid up in cool room temperature conditions 15-20°C. The tack of the prepreg is greatly affected by the ambient temperature. Lower temperatures will reduce the surface tack .The more commonly known and used autoclave heats the pressure vessel that uses high pressure to process and cure materials. Autoclaves require a large amount of capital investment. They use up a lot of energy, are expensive to run, and limit the component size. Autoclaves also do not allow in-process . See more
medial meniscus tear diagnostic test|special tests for meniscus tear